The two most common questions I hear from readers are, how can I build a tiny house and how much does a tiny house cost. Both of these questions are tied together and I’ll answer both in this post.
The following is an overview of what you’d need to do to build a tiny house for yourself. To do this topic justice I’d have to write hundreds of pages, but I think this outline should give you a good idea of what’s involved. I think you’ll also see that it is a project within reach of many do-it-yourselfers.
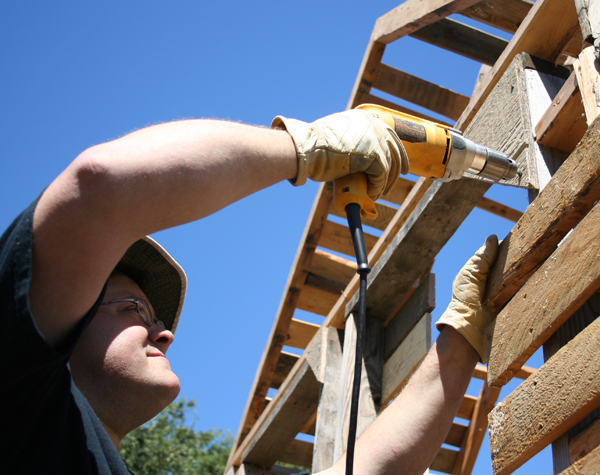
Above: Working on my Tiny Free House.
1. Design your tiny house
Keep the design simple if you are planning on building on a tight budget or have limited experience. Avoid things like dormer windows and complex roof lines. Avoid complex walls, wide window and door openings, porches, and excessive ornamental features. Each tiny complexity in the design can add many hours of work and hundreds of dollars in materials.
You can buy plans or come up with your own design. I offer several free tiny house plans and a selection of low-cost tiny house plans.
If you choose to design your own tiny house I recommend using SketchUp to help turn your ideas into measured drawings you can build from. Once you have your design in hand, it’s time to make a materials list and go shopping for building materials.
2. Acquire and prepare a trailer
The first step is to find a place to build the house. If you choose to build on a trailer, owning land is not a requirement. It does help to have a place to build the house where you have ample space to work and friendly (not likely to complain) neighbors. Tiny houses can be as tall as a semi-trailer, 13.5-feet, so it’s a project that needs a lot of fair weather or a large warehouse-like workspace.
Tiny houses are heavier than normal travel trailers because they are built like houses, so they need to be built on stout trailers. The most common type of trailer used is a simple dual-axle flatbed trailer with trailer breaks. Expect to spend between $2,000 and $4,000 for a new flatbed trailer. The cost increases as the weight capacity and size increase.
Used trailers can be a better bargain but are a bit harder to find, and like anything used, harder to determine if the weight capacity and overall condition of the springs, axles, coupler, etc, are up to the job. I used a free used trailer for the Tiny Free House, which made a lot of sense for a free house project, but I’ll buy a new trailer for the next house I build which I hope to be an ultralight tiny house.
3. Build the floor
The trailer is your foundation when you choose to build a mobile tiny house. The next step is to build your floor with standard lumber, secure the framing to the trailer, insulate, and sheath it with plywood or OSB (oriented-strand-board). Both plywood and OSB are extremely durable, but OSB typically costs a little less.
Attaching the framed floor to the trailer in an important step. Each trailer is a little different so there is no single right way to make this connection. Using metal brackets, nuts & bolts, and u-bolts are common methods. If in doubt add more fasteners.
4. Prepare for utilities
Drains and wiring that must run through the floor should be installed now. If you’re adding RV waste and potable water tanks this is a good time to add those too. Some folks add them later by crawling under the house but by planning ahead you can help you avoid extra work later.
If you choose to use a composting toilet, which many people do, there is no need to have a black water (sewage) tank. You will still need some way to handle the grey water from the sink(s) and shower. The shower location and drain installation is also best at this time.
Few tiny houses are built with laundry facilities, but this may be a good time to think though the waste lines for a clothes washer too if you plan to have one.
5. Frame the walls
This is the step where the house takes shape. Framing the walls will go fast and you’ll feel like you’re making speedy progress. It will also feel like quite an accomplishment to have the walls up and sheathed with plywood or OSB.
Many tiny house builders will also use hurricane strapping and other metal brakets to hold the roof firmly to the walls and the walls firmly to the floor. This metal bracing is not visible when the house is complete but works inside the walls to keep everything together.
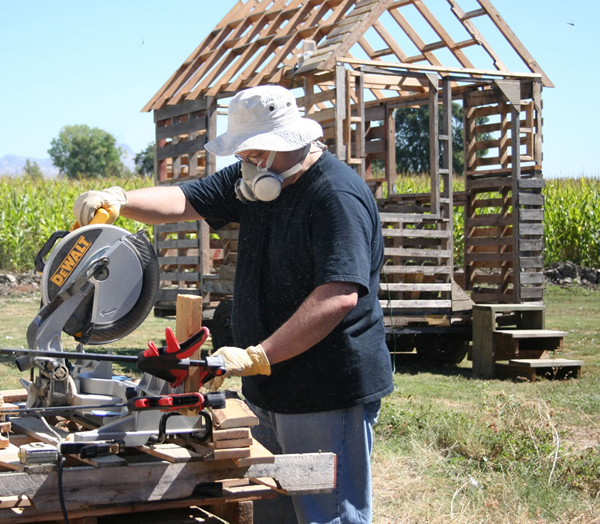
6. Frame the roof
Once the walls are up you’ll be ready to put the roof up. Roof framing is tricky because you’re working up high and you’re building something more complex than strait walls. Tiny houses may look small but when you’re up on top of one you’ll realize that working above ground at 10′ to 13′ isn’t as easy as it looks.
You’ll also thank your frugal intuition at this time if you chose to build a simple roof. Dormers and hip roofs are beautiful when complete, and may be worth the extra effort for some folks; but if you’re new to construction or want to get your project done quickly simpler roof designs may be a better choice.
7. Install the roofing material
Once the roof is framed and sheathed you’ll want to put on the roofing material that will keep the rain out. I highly recommend using standing seam metal roofing because it lasts an incredibly long time and is ideal for rain water collection. Metal roofs will also hold up well under the high winds you’ll experience on the highway.
The steeper and more complex your roof the harder it will be to install. You’ll notice that many tiny houses use a 12/12 pitch (45-degree angle), which is actually a very steep pitch. Choosing a shallower pitch will be easier and safer to install.
8. Wrap it up
Now it’s time to wrap it in house wrap, a breathable material that keeps the walls dry and protected from the elements while allowing moisture to escape. You’ll also use a special tape to seal the seams to provide additional weather proofing.
9. Windows & doors
Installing windows and doors should only be done when you are well rested and in a patient mood. It’s also handy to have help because you don’t want to drop one out the side opposite you, and you’ll find it very useful for wiggling it into place.
You see the trick with windows and doors is that you must get them perfectly level and square. Even in a tiny house on wheels this is important because it will increase the longevity and function of the doors and windows.
You’ll also use the house wrap tape to seal around the windows and doors to add an additional seal. Water can work it’s way inside the walls and house, especially at high speed on the road or in a storm. So it’s really important to take great care with all the seals.
Windows and doors can also be a major expense. If you want to keep costs low I suggest shopping the secondary market. You’ll find that McMansion projects produce a lot of waste and put a lot of lightly damaged materials on websites like craigslist. You may even find a building materials store in your area that specializes in this kind of stuff. So before you finalize your design and start framing the walls you should really have your windows and doors purchased.
10. Exterior cladding, trim, paint, caulk.
Some people will actually sheath the exterior of the house with a paintable (or pre-finished) material that doubles as cladding, so adding another layer of cladding/siding is not always needed. For example, exterior grade plywood can be painted and serve as the cladding. You can also use fibrous concrete board, like Hardie Board, as a single layer exterior sheathing and cladding.
You’ll also add your exterior trim at this point and then finish up by painting the exterior of your house. Caulking any gaps will also help to keep water out of your walls.
11. Rough-in plumbing
Your house is now sealed from the elements but the interior is still unfinished open-framed walls. This is also where the real slow work begins.
The first step is to rough-in the plumbing. This simply means that you are putting drain and supply pipes in the walls and floor. You’ll also be adding your water heater at this point. If you’re using waste and potable water tanks like an RV, you’ll be adding them now if you didn’t add them when you built the floor.
There are a lot of plastic pipes products available and they make plumbing a house super easy but I suggest sticking with copper. It costs a little more money and is harder to work with but the house is small you’ll soon be done. I also have a bias against plastics because it seems like every time I turn around we learn about another heath concern connected to plastics.
What doesn’t happen at this stage is the addition of faucets and other fixtures. But you will want to pressure test your water lines before continuing. Can you imagine sealing up the walls and then discovering a leak? If you have a friend that’s a plumber this might be a good moment to ask for help.
12. Rough-in electric
I like to do the rough-in plumbing before the rough-in wiring because wires bend around wall cavities easier than pipes. Rouging-in electric wiring is simply running wire through small holes drilled in the framed walls. You connect the wires inside junction, outlet, and switch boxes in the walls. It’s not rocket science but it’s incredibly important to do this step right because sparks from improperly installed wiring can cause fires. If you have a friend that’s an electrician this an excellent moment to ask for professional help.
13. Insulate
There are many different kinds of insulation and there is no one single way to insulate a tiny house. But most people seem to prefer using foam board. Look for low-VOC (volatile organic compound) board because it will keep the interior air quality of the house healthier. The real trick with insulation is stopping the radiant heat and air leaks. When you insulate you have an opportunity to fill all the tiny cracks and crevices. Expanding spray foam and plastic sheeting can help make this easier.
Some people will also use a couple different layers of different types of insulation. For example, a reflective barrier next to the exterior sheathing will help slow down radient heat allowing the foam board to work on stopping heat flow.
14. Interior sheathing
Once the walls are insulated and all the rough-plumbing and rough-wiring is complete, it’s time to seal up the walls. You’ll notice that many people like to use wood on the inside of tiny houses but there is no reason you can’t use drywall. Some suspect that drywall will eventually crack due to vibrations during transportation but others tell me that they’ve had no problems with drywall. The other advantages of drywall is that it provides a bit of additional fire protection and costs very little.
15. Interior trim & built-ins
Once the walls are covered it’s time to do the finish carpentry inside which includes any cabinets, built-ins, and trim. This is slow careful work and can take a bit of time. If you don’t have a lot of experience with carpentry you may want to find a friend of pro who can help. This is also one area where costs can shoot up especially if you select high cost items like stainless steel counters.
16. Interior paint & stain
Once the final wood work is complete it’s time to apply the final finishes, like paint, stains, and sealers to your walls and wood surfaces. This is also slow careful work but can be completed fairly quickly.
17. Finish electric
Now that the walls are finished it’s time to add your electric outlets, switches, and fixtures. If you have a friend that’s an electrician this might be a good moment to ask for help. If you’ve chosen to have an off-grid solar electric system this may also be the best time to finish installing it.
18. Finish plumbing
Just like the electrical finish work, it’s time to finish up the plumbing by installing faucets and other fixtures. If you have a friend that’s a plumber this might be a good moment to ask for help, but these final steps are not as difficult as putting the pipes in the walls.
19. Finish flooring
The last step is to cover that plywood subfloor with a real flooring material. Wood flooring seems like the most logical material to use except in the bathroom and possibly the kitchen. Pre-finished wood floors install quickly and it’s affordable. Shop around and you might even find leftovers from another project that can completely cover your tiny floor.
20. Move in!
One of the biggest differences between building a tiny house on a trailer and building on a permanent foundation is that you’ll most likely avoid building permits and inspections. But don’t get me wrong, it’s a very good idea to follow building codes because they describe best practices that can help you build a safe house.
The main areas you can save money are:
- Trailer – Shop carefully and save $1,000 or more.
- Exterior Siding – Consider a single layer material like Hardie Board.
- Interior Sheathing – Consider drywall over wood. It’s not as warm and cozy but costs less.
- Windows & Doors – Buy seconds at significant discounts.
- Interior Decor – Stainless steel looks great and lasts lifetimes, but if you’re short on initial cash consider the frugal route initially. You can always remodel/resurface.
- Flooring – There are many bargains to be found in flooring in the new and secondary markets.
- Appliances – Those stainless steel marine fireplaces look and function great but cost $1,000. Make frugal choices here and save a lot. You can always upgrade later.






Nice write up Michael. You might get some more that want to build the solar house.
Thanks Bill!
As an experienced tiny house builder let me know if I missed anything 🙂
(Bill is building a house from one of my free tiny house plans, the 8×16 Tiny Solar House. https://tinyhousedesign.com/free-plans/)
Thanks for the vote of confidence Michael. There are probably a few things I would change in building another, but the plan is a great starting place. I will have to write some of these down for you later.
I wonder how the tiny solar house would be with a vardo or rounded roof on it instead? It could give you more space in the loft area, and maybe be a bit easier on constructing the walls. Of course the roof part would be a bit trickier with that method.
This is a nice starting point for anyone wanting to build one. I hope we see more people start their own house soon.
nice article- smart man…very thorough-informationally loaded! Great job Michael!
-Deek
Relaxshacks.com
I really appreciate that you put this information up. I have been seriously considering building a tiny house on a trailer to live in with my three year old daughter. I am a college student on public assistance and tired of living this way and getting nowhere. I am already dissatisfied with my career choice but the one I would really like does not pay the salary I would need to live better than I do now. It has always been a catch-22 for me and I am sure I am not alone in this either, but a tiny house gives me hope because I know how to live with very little already and a tiny house will give me so much more in many ways. Thanks again for the information, especially about the google sketchup because I am designing my own house and that will be a great help.
I hope you do get a chance to build or purchase your tiny house Sarah. Michael’s tiny solar house plans are a great starting point. He has the basic frame laid out, so you can focus on the internal layout of your house.
Good luck and let us know what you end up doing.
Even though I don’t think of building my own tiny house your recipe is very informative and detailed. After reading it seems that maybe even I could build it. Great job Michael.
It is not as hard as it seems, once you do some reading on the topic. There are some excellent books out there for building houses. One is how Habitat for Humanity typically builds a house. There are a few others I bought as well. Until I began building my solar house, I had not built any either. Now that it is almost done, it is kind of amazing to see. There are things I would do a bit different next time, but it has been a great learning experience.
Hi, just need some input. I LOVE the tiny home, have for along time and seriously thinking of starting on purchasing a trailer. Than I start to think why not just get an RV?? Help please with pros and cons, thanks Deb.
Good advise and a good read
Cheers Stewart
http://tinytugboat.blogspot.com/
I will be taking on this project THIS weekend.. I hope!!!
This blog post was really helpful. I found it while searching for info on roof pitch. I still don’t understand why almost all tiny house plans on a trailer use a 12/12 pitch (45-degree angle) for the roof. Does anyone know, what is the minimum degree the pitch has to be? I want to have optimal head room space for my loft areas.
The 12/12 pitch is just an aesthetic choice. The minimum pitch and the chosen the roofing material go hand-in-hand. For example if a really shallow pitch is desired some kinds of roofing material will not work, like shingles.
Also be aware of snow loads. A 12/12 pitch is steep, but it’s great for shedding snow.
Thank you! Building a Vardo is a dream of mine. Question …could I use a modified boat trailer as a base? Thanks again… newbie Tracy
I saw somewhere that you had a SketchUp model of a flatbed trailer with fenders somewhere. Can you let me know where that is? I see there’s a flatbed above the wheels, but I’m looking for the one you use in your tutorials.
Thanks,
I have a newer version. Try this: https://tinyhousedesign.com/sketchup/18-foot-trailer.skp
Canyon Rim Tiny Houses is an up and coming Tiny House company that believes in the Tiny House movement. We have been in the construction company for over 25 years and are now building tiny houses! Please check us out and let us know what you think at http://www.tinyhousesforsalecanyonrim
This is a super helpful post, thanks for the tips. I’ve been looking at building myself a tiny home for a few years. Now that I’m done college I’ve started looking into it more seriously. I have a question about insulation. I’ve read about foam board a bit online and like it’s connivance, but I live in Canada and at times it can drop to -40 degrees would it supply enough warmth or should I look into other methods, and what might those other methods be?
I am in the process of purchasing land to be able to build a tiny house. I am really excited about the prospect. Thanks so much for the information on this page – I am sure it will come in handy when the building project starts 🙂
In #10 you explain, “For example, exterior grade plywood can be painted and serve as the cladding. You can also use fibrous concrete board, like Hardie Board, as a single layer exterior sheathing and cladding”. Am I understanding this to mean that in using exterior grade plywood as opposed to regular plywood sheathing over your framing, there would be no use / need for house wrap? Would the house be as ‘water tight’ without the all-over house wrap? I’d consider / look in to this option if it would be worth while (and I wouldn’t be giving any thing up as far as it’s soundness regarding water / leakage) to get my build done for less cost initially. Later, once recouped from the initial build expenses, I could install something more attractive and more detailed if I wished.
No, I would use housewrap in both cases. If you use exterior siding sheathing then place the housewrap directly on the wood framing.